Pyrolysis
Definition
Historical
- Amazon moundculture
- Mummy methanol
Technical
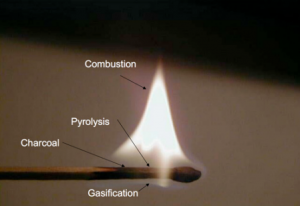
Although it seems counterintuitive, wood actually does not burn. Instead it is the gas emitted by heating the wood that burns. Only when the wood is finally charred under the flame of the woodgas, can oxygen penetrate the then porous structure of the newly charred wood and glow the carbon to ash. Striking a match on the rough surface of the matchbox ignites a flaming chemical reaction of the sulfurous tip that generates enough heat to make the wood emit highly combustible gases. The flame ignites the gases so released from the wood and the process continues under the heat from the burning pyrolysis gases, causing further outgassing and burning of gas. But underneath the flame of the woodgas the wood itself does not burn but carbonizes, because the gas flame consumes all the oxygen, creating a pyrolysis zone where the flame protects the match from oxidation. As we know, the match burns with a clean flame until someone blows out the flame after which it will smoke. The smoke is just the last unburned and condensing residual wood vapors, released before the match cools sufficiently to stop outgassing them. [1]
Processes
To transform feedstocks into biochar, in any form, involves a lot of heat with limited exposure to oxygen.
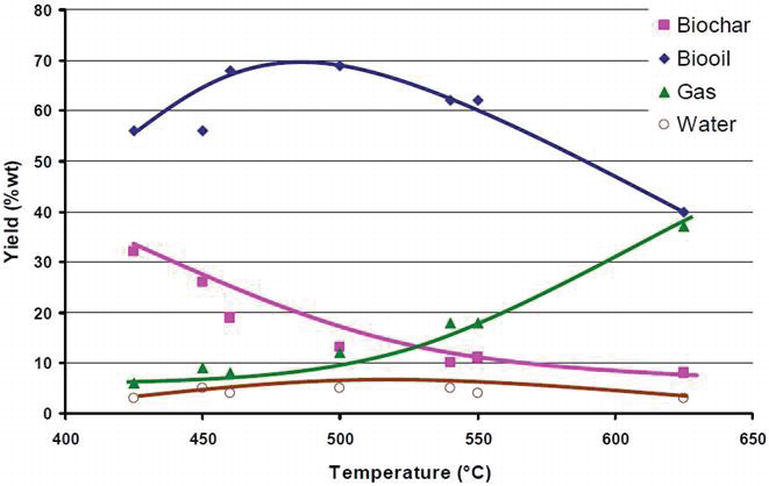
Fire will reduce biomass to ash in the presence of oxygen. Deprived of air, however, the thermal decomposition process separates biomass into gases, liquids, oxygenated compounds (e.g., methanol), and solid (biochar). The ratio between these components, given a particular feedstock, will depend on the conditions of its heating. Generally speaking, lower and slower burns will yield more char, while hotter or shorter processes yield oils and gases potentially useful as biofuel.
The nested sections below offer practical details on these different processes.
- Effective charring can require preparation of the feedstocks, through drying and/or size reduction, making dead or waste materials often the most ideal candidates. Pretreatment may be necessary, however, depending on the feedstock and reactor in question.
- The final step of any process is its quenching, in which the fire is put out and the char itself better activated, most often with water but sometimes with urine or dirt.
Section content, unless otherwise cited, sourced from Amonette, J.E., et al. 2021. Biomass to Biochar: Maximizing the Carbon Value. Report by Center for Sustaining Agriculture and Natural Resources, Washington State University, Pullman WA.[2]
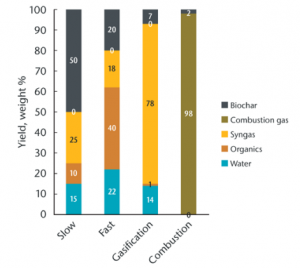
Bullet point data mostly taken from Journal of Analytic and Applied Pyrolysis 2022 (in which "yield" refers to biochar weight).[3]
Torrefaction
- 200-300 °C
- 10-60 minutes
- 70-90 % yield
- Good for biocoal
Torrefaction is also called mild pyrolysis, as it still involves heating biomass in an "inert" or oxygen-deficit environment, but only to a maximum temperature of 300°C. The biomass will evaporate both its water content and some volatile organic compounds. This process yields a uniform product of lower moisture, and higher energy content, than raw biomass. It is also easier to grind due to its brittle quality. [4]
Slow Pyrolysis
- 300-800 °C
- minutes to days
- 25-35 % yield
- Good for biochar
Slow pyrolysis, also called conventional carbonization, produces biochar by heating biomass at a low heating rate (around 5-7 °C per minute) for a relatively long residence time and typically uses large particles. These conditions produce less liquid and more biochar than fast pyrolysis. In general, slow pyrolysis requires less pretreatment of the feedstock than fast pyrolysis.
Fast Pyrolysis
- 400-700 °C
- 0.5-10 seconds
- 12-15 % yield
- Good for biooil
Fast pyrolysis describes heating rates of over 300 °C/min., which are typically used to obtain high yields of single-phase bio-oil. Fast pyrolysis uses small particles, generally smaller than 5 mm in diameter, due to the low thermal conductivity of lignocellulosic materials.
Gasification
- 750-1000 °C
- seconds to hours
- 5-10 % yield
- Good for biogas
Gasification differs from pyrolysis in that some oxygen is present at much higher temperatures (>750 °C). Gasification has been used since the 1800s in energy generation from coal and biomass. Gasification converts carbon-based materials into carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide (syngas or producer gas). The gas mixture can then be combusted to generate power. While gasification technologies were designed for power, rather than biochar production, biochar can be produced with this approach.
Combustion
- 1000-1200 °C
- 1-2 % yield
- Good for heat
Biomass is fired and allowed to breathe, producing gases to be burned up as biomass ashes, thus driving the continuation of the process. Reactors relying on combustion are primarily designed for generating heat, commonly used for a combination of steam turbine electrical generation and secondary heat uses such as curing lumber or drying grain.
Though the word combustion seems antithetical to the production of biochar, it is ironically combustion -- that ordinary, everyday technology -- that is perhaps responsible for a majority of biochar produced on Mother Earth. The key is that not all combustion technologies result in 100% complete combustion (yielding ash as the sole solid product); indeed, combustion technologies are imperfect. When oxygen is present, but insufficient for complete combustion, biochar can be pulled out of the system. Combustion for a boiler will generally yield 1.5-2% biochar.
https://permanent.fdlp.gov/gpo129286/fpl_gtr270.pdf