Biochar
OVERVIEW COPY TEXT
Definition
Historical
Origins

For over 9000 years, Indigenous Peoples in the Amazon Rainforest enriched the forest soil surrounding their villages using biochar.[8][9] In a compost mix with other amendments, the use of biochar by Indigenous farmers created highly fertile and nutrient-rich soils known as yana allpa (Quechuan: "black earth"), more widely known by the Spanish term "terra preta" today.[10]
Yana allpa is visibly distinctive via the noticeable presence of black carbon in the form of biochar, which exists in concentrations around 70 times greater than surrounding soils.[11] Its high nutrient profile, cation exchange capacity, and more balanced pH also stands in sharp contrast to oxisol, the less fertile and highly acidic yellow soils which grow throughout most of the Amazon.
The disruption of Indigenous biochar cultivation and yana allpa generation by the onset of European colonization severely fragmented and destroyed Indigenous knowledges regarding these practices. As a result, much of what is known about yana allpa today is the result of archaeology:
1. Fieldwork has shown that yana allpa sites are widely distributed across the region and most likely to be near the Amazon River. They have persisted in their fertility and distinctiveness for thousands of years.[12] The longevity of yana allpa is a core body of evidence empirically demonstrating biochar's long-term carbon sequestration abilities.
2. Yana allpa sites, now largely overgrown, once had fewer towering trees, but were heavily populated by numerous shorter fruit trees. Yana allpa is so closely associated with evidence of concentrated human residence -- such as handmade ceramics and the remains of fortified villages -- that archaeologists were forced to revise upwards their estimates of pre-colonial Native populations by millions of more people.[13] The existence of large villages and cities in the Amazon which had been attested to by early reports, but subsequently dismissed following their destruction amid the genocidal violence of European colonization, has consequently been supported by this evidence.[14]
Revival
Technical
Biochar is an output of pyrolysis. Any quantity of biomass (organic feedstock given for pyrolytic reduction) can yield carbon in this highly compressed solid form.
Importantly, the value of the char comes not only from what it contains, but also from what it does not (yet) contain. That is, the porous structure of its carbon content makes biochar act like a microscopic sponge. [15] Following this distinction, the two sections nested here provide further definition for "positive" vs. "negative" spaces of a biochar:
Crystals
Biochar is the most stable form of organic carbon known to exist in the terrestrial environment.[16] This is due to the fact that it is a crystalline solid with a high degree of orderliness in its molecules. The biochar process (burning within a low-oxygen environment) results in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds that do not easily break. These bonds give biochar its stability and -- being structured like graphite rather than diamond -- its black color[17][18]. Biochar's high stability means that it resists decomposition in soils and therefore can serve as a long-term (1000+ year) storehouse for carbon.[19]
Cavities
While the stability of biochar is an important attribute, it is the porosity of biochar that gives it many of its unique properties. The pores in biochar can be classified as either micropores (<2 nm in diameter), mesopores (2-50 nm), or macropores (>50 nm).[20] Being highly porous, Biochar has a high surface area to volume ratio (upwards of 340 m2/g). [21] This gives biochar a large internal surface on which various chemical and biological processes can take place. For instance, biochar's porosity allows it to act as a sponge for water and nutrients, while serving as a substrate for the growth of microorganisms.
ADSORB vs ABSORB:
Production
Feedstocks
Any biomass can -- theoretically -- become biochar. The most famous example, charcoal, simply refers to biochar for which wood is the feedstock. There are at least as many different feedstocks as there are flora.
Biomass waste materials appropriate for biochar production include wild detritus, crop residues (both field residues and processing residues such as nut shells, fruit pits, bagasse, etc) and animal manures, as well as yard and food wastes. [22]
The nested sections below organize this plentiful array of resources according to their location in wild, rural and urban ecologies, respectively.
Feedstock can be further classified as dry or wet. Feedstock with moisture content under 30% after harvesting is dry; this includes branches, waste wood or agricultural residues. Feedstock with moisture content above 30% is considered as wet biomass; this includes algae, animal/human excreta and sewage sludge. [23]
Special characteristics of a given feedstock, in terms of its preparation and its biochar product, are detailed below.
<<Forest / Plains>>
- Hardwoods
- Alder - Balsa - Beech - Hickory - Mahogany - Maple - Oak - Teak - Walnut
- Softwoods
- Cedar - Fir - Douglas fir - Juniper - Pine - Redwood - Spruce - Yew
- Grasses
- Switchgrass - Bamboo - Ditch Weed
<<Farm / Pasture>>
- Crop residues
- Straw - Corn - Rice
- Animal manures
- Chicken - Swine - Human
<<Municipal / Industry>>
- Yard waste
- Grass Clippings - Sticks or Twigs - Woodchips - Sawdust
- Food waste
- Fruits
- Biosolids
- Paper - Pulps - Sewage sludge - Digested sludge
Processes
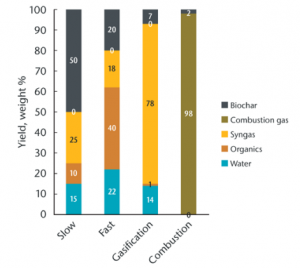
To transform feedstocks into biochar, in any form, means applying a great deal of heat while limiting exposure to oxygen.
Fire will reduce biomass to ash in the presence of oxygen. Deprived of air, however, the thermal decomposition process separates biomass into gases, liquids, oxygenated compounds (e.g., wood vinegar), and solid (biochar). The ratio between these components, given a particular feedstock, will depend on the conditions of its heating. Generally speaking, lower and slower burns will yield more char, while hotter or shorter processes yield oils and gases potentially useful as biofuel.
The nested sections below offer practical details on these different processes.
Regardless of process pursued, effective charring usually requires preparation of the feedstocks, most often both drying and size reduction. The particulars of this pre-process treatment, plus the possibility of harnessing it as a natural feedback from the heating process itself, depends on the feedstock and reactor in question.
Section content, unless otherwise cited, sourced from Amonette, J.E., et al. 2021. Biomass to Biochar: Maximizing the Carbon Value. Report by Center for Sustaining Agriculture and Natural Resources, Washington State University, Pullman WA.[24]
Bullet point data mostly taken from Journal of Analytic and Applied Pyrolysis 2022 (in which "yield" refers to biochar weight).[25]
Torrefaction
- 200-300 °C
- 10-60 minutes
- 70-90 % yield
- Good for biocoal
Torrefaction is also called mild pyrolysis, as it still involves heating biomass in an "inert" or oxygen-deficit environment, but only to a maximum temperature of 300°C. The biomass will evaporate both its water content and some volatile organic compounds. This process yields a uniform product of lower moisture, and higher energy content, than raw biomass. It is also easier to grind due to its brittle quality. [26]
Slow Pyrolysis
- 300-800 °C
- minutes to days
- 25-35 % yield
- Good for biochar
Slow pyrolysis, also called conventional carbonization, produces biochar by heating biomass at a low heating rate (around 5-7 °C per minute) for a relatively long residence time and typically uses large particles. These conditions produce less liquid and more biochar than fast pyrolysis. In general, slow pyrolysis requires less pretreatment of the feedstock than fast pyrolysis.
Fast Pyrolysis
- 400-700 °C
- 0.5-10 seconds
- 12-15 % yield
- Good for biooil
With fast pyrolysis, the process of heating biomass is rapid (heating rates of over 300 °C/min). Fast pyrolysis is typically used to obtain high yields of single-phase bio-oil. Fast pyrolysis uses small particles, generally smaller than 5 mm in diameter, due to the low thermal conductivity of lignocellulosic materials.
Gasification
- 750-1000 °C
- seconds to hours
- 5-10 % yield
- Good for biogas
Gasification differs from pyrolysis in that some oxygen is present and much higher temperatures are used (>750 °C). Gasification has been used since the 1800s in energy generation from coal and biomass. Gasification converts carbon-based materials into carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide (syngas or producer gas). The gas mixture can then be combusted to generate power. While gasification technologies were designed for power, rather than biochar production, biochar can be produced with this approach.
Combustion
- 1000-1200 °C
- 1-2 % yield
- Good for heat
Biomass is fired and allowed to breathe. Resulting gases are burned up around ashes of the biomass, thus driving the continuation of the process. Reactors relying on combustion are primarily designed for generating heat, which is commonly used for a combination of steam turbine electrical generation and secondary heat uses such as curing lumber or drying grain.
Though the word combustion seems antithetical to the production of biochar, it is ironically combustion -- that ordinary, everyday technology -- that is perhaps responsible for a majority of biochar produced on Mother Earth. The key is that not all combustion technologies result in 100% complete combustion (yielding ash as the sole solid product); indeed, combustion technologies are imperfect. When oxygen is present, but insufficient for complete combustion, biochar can be pulled out of the system. Combustion in a boiler will generally yield 1.5-2% biochar.
Reactors
Nesting Cookstove
- How-To Guides:
Basic design, built entirely from soup cans and other household materials, developed for elementary students at the Dome School (Oregon, USA) [27]
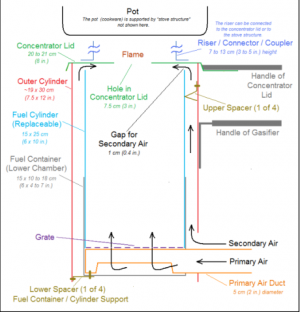
Flame-Cap Kiln
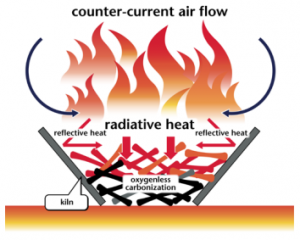
A flame-cap kiln is a simple container that can be made from an earthen pit, bricks or ceramics, and metal. Only the metal kilns are portable. Kilns can have any shape, including cylinders, cones, pyramids, rectangles, or troughs. Their width:height ratio should be 1:1 or greater; 2:1 is recommended. A kiln that is too tall will have trouble getting enough air to maintain combustion.
These kilns operate according to the principle of counterflow combustion. All combustion air comes from above, feeding a flame that is always maintained. The flame heats the feedstock below by radiation, which emits gasses that are burned in the flame. The flame consumes all the available air, so that no air is available to burn the char that forms beneath the flame.
The counterflow combustion air keeps the flame low and prevents emission of embers or sparks. The flame also further combusts organic compounds in the smoke, reducing emissions of harmful compounds. Periodically, new feedstock is loaded into the kiln. This temporarily interrupts the flame-cap which is quickly reformed. Once the kiln is full of char, it is quenched either with water or by snuffing with a lid.
Flame-cap kilns can be loaded by hand. Stewards require training to do this with the highest efficiency and lowest emissions. If loaded too fast, the flame front moves upward and the radiant heat from the flame is not able to char all of the feedstock. If loaded too slowly, more of the material may burn to ash. For these reasons, as well as their own safety, kiln workers must be aware of feedstock species, size and moisture level and must be able to adjust loading rates and practices accordingly.
With properly cut and dried feedstocks, the biochar conversion efficiency of a flame cap kiln can rival that of industrial pyrolysis kilns. If well managed, a flame cap kiln can convert biomass to biochar with an efficiency of up to 40% by weight.
This reactor requires no external energy inputs for heating.[28]
- How-To Guides:
Step-by-step illustrated guide [35pg] for building and operating a soil-pit (or metal) flame-cap kiln[1]
Step-by-step video guide [3:07m] for building and operating a cylindrical "ring of fire" flame-cap kiln[2]
ecovillage power plant deal
Application
Carbon Sequestration
Biochar has been identified as a key means of sequestering (removing and storing) carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, either into the Earth's soil or products made from Biochar. A group of scientists published in Nature in 2019 identified Biochar as the negative emissions technology "at the highest technology readiness level." [29] According to their research, the global carbon sequestration potential of biochar (when also using potassium as a low-concentration additive) is over 2.6 billion tons of CO2/year.
Projects
Soil Amendment
Biochar increases long-term soil organic carbon content in a form which can endure for thousands of years, as seen in the Amazonian Black Earth.
Additional benefits of Biochar for soil include improved soil texture, nutrient retention, cation exchange capacity,[2] water retention,[3] and microorganism habitat.[4]
Projects
Feed Additive
Livestock farmers increasingly use biochar as a regular feed supplement to improve animal health and increase nutrient intake efficiency. As biochar gets enriched with nitrogen-rich organic compounds during the digestion process, the excreted biochar-manure becomes a more valuable organic fertilizer causing lower nutrient losses and greenhouse gas emissions during storage and soil application.
An analysis of 112 scientific papers on biochar feed supplements has shown that in most studies and for all farm animal species, positive effects could be found on different parameters, such as:
- growth
- digestion
- feed efficiency
- toxin adsorption
- blood levels
- meat quality
- gas emissions
However, a relevant part of the studies obtained results that were not statistically significant. Most importantly, no significant negative effects on animal health were found in any of the reviewed publications. [30]
Projects
Water Filter
Charcoal has been a part of water treatment for at least 4000 years.[31] Biochar’s incredible porosity and surface area give it a high capacity to adsorb a wide variety of contaminants from water.[32]

Laboratory testing shows that biochar can effectively reduce contaminants including:
- Heavy metals like lead, copper, zinc, cadmium, cobalt, and nickel;
- Organics such as gasoline compounds and other volatile organics, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB), polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), and some herbicides, pesticides and pharmaceuticals;
- Chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biological oxygen demand (BOD);
- Nutrients such as phosphorus and ammonia;
- Totals suspended solids (TSS).[33]
A 2019 study found that using biochar in modified sand filters for wastewater treatment would be just as effective as other methods in removing microbes while significantly reducing the amount of land needed, a major obstacle to wastewater treatment on small farms.[34]
How To Guides:
18 minute video guide for making a medium-large (one or multi-barrel) water filtration system using biochar [3]
10 page manual on building a multi-barrier water filtration system (including biochar)[4]
Projects
Supercapacitor
The fabrication of biochar-based materials with excellent electrochemical behavior as a "supercapacitor" can be sustainable and low cost.[35]
These capacitors are endowed with excellent reliability, high power density, and fast charging/discharging characteristics. Supercapacitors are thus utilized in a wide range of applications, particularly in electrical vehicles.
Biochar has been established a potent material of interest for electrochemical energy storage and conversion in this way. However, research needs to be carried out in resolving a few outstanding issues. For large scale and cost-effective deployment, the conversion efficiency and quality of biomass into biochar are required to be maintained without additional steps for treatments, while biochar functionalization (i.e. surface oxidation, amination, sulfonation etc.) should avoid intricate operations and toxic chemicals to retain a green solution. [36]
Sources
[1] <https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-019-41953-0>
[2] <https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/11/11/3211/pdf>
[3] <https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2015.00733/full>

![Step-by-step illustrated guide [35pg] for building and operating a soil-pit (or metal) flame-cap kiln[1]](/wiki/images/thumb/3/39/Making_Biochar_Guide_1.png/320px-Making_Biochar_Guide_1.png)
![Step-by-step video guide [3:07m] for building and operating a cylindrical "ring of fire" flame-cap kiln[2]](/wiki/images/thumb/5/5d/Ring_of_Fire_Kiln_Guide.png/320px-Ring_of_Fire_Kiln_Guide.png)
![18 minute video guide for making a medium-large (one or multi-barrel) water filtration system using biochar [3]](/wiki/images/thumb/9/99/Biochar_Water_Filter_Video_Guide.png/320px-Biochar_Water_Filter_Video_Guide.png)
![10 page manual on building a multi-barrier water filtration system (including biochar)[4]](/wiki/images/thumb/e/e5/Multi-Barrer_Biochar_Filter_System.png/276px-Multi-Barrer_Biochar_Filter_System.png)